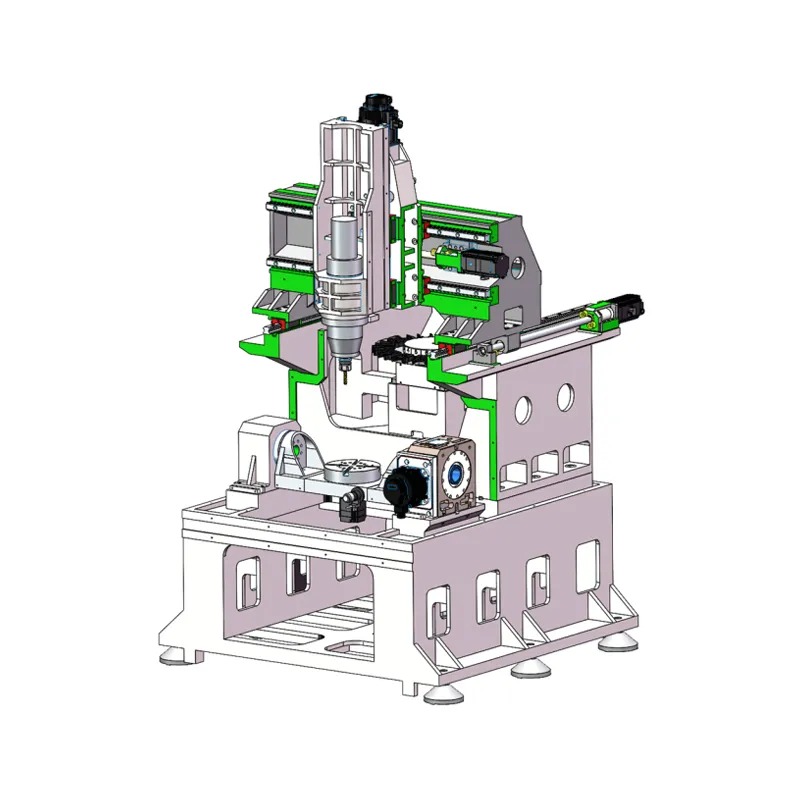
CNC lathes are essential tools in modern manufacturing, enabling precise turning, cutting, and shaping of materials like metal, plastic, and wood. As a cornerstone of the CNC machining industry, these machines come in various types, each tailored to specific applications and production needs. Whether you’re a manufacturer, hobbyist, or industry professional, understanding the different types of CNC lathes can help you choose the right machine for your projects. In this guide, we’ll explore the most common types of CNC lathes, their features, advantages, and applications.
What Is a CNC Lathe?
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathe is a machine tool that uses pre-programmed instructions to control the movement of cutting tools and workpieces. Unlike manual lathes, CNC lathes automate the turning process, ensuring high precision, repeatability, and efficiency. The workpiece rotates while the cutting tool moves along multiple axes to create cylindrical parts, such as shafts, bolts, or intricate components.
CNC lathes vary in complexity, from basic 2-axis machines to advanced multi-axis systems. Below, we’ll break down the main types and their unique capabilities.
Types of CNC Lathes
2-Axis CNC Lathes
Overview
The 2-axis CNC lathe is the simplest and most common type. It operates along two linear axes: the X-axis (horizontal movement) and the Z-axis (longitudinal movement). The workpiece spins while the cutting tool moves to shape it.
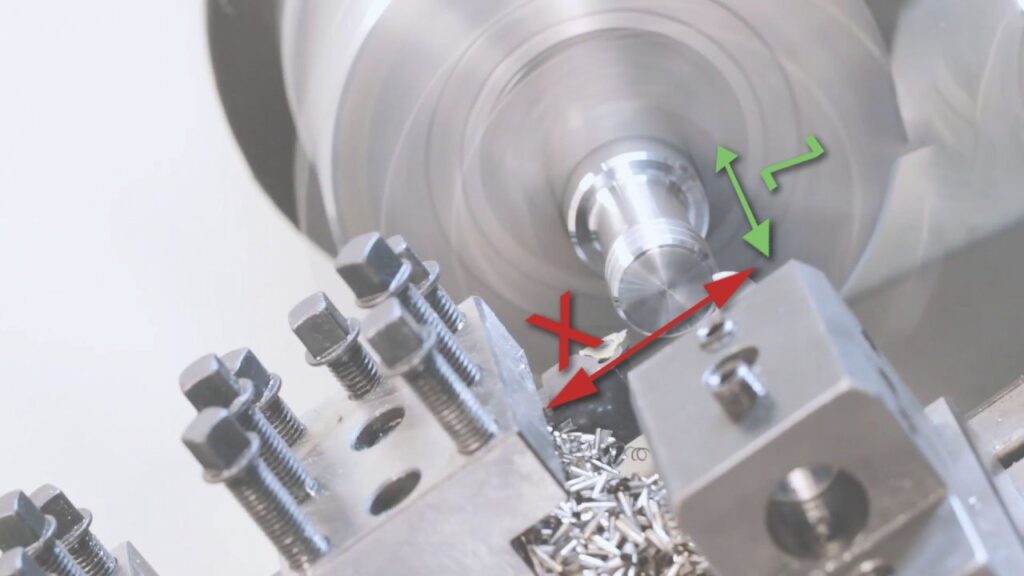
Features
- Basic turning operations (e.g., facing, threading, drilling).
- Single-tool setup.
- Ideal for simple cylindrical parts.
Advantages
- Cost-effective and easy to operate.
- Suitable for small to medium production runs.
- Low maintenance requirements.
Applications
2-axis CNC lathes are widely used in industries like automotive and aerospace for producing straightforward components such as bushings, pins, and spacers.
3-Axis CNC Lathes
Overview
Building on the 2-axis design, 3-axis CNC lathes add a third axis (typically the Y-axis), allowing for more complex machining. This extra axis enables off-center milling and drilling operations.
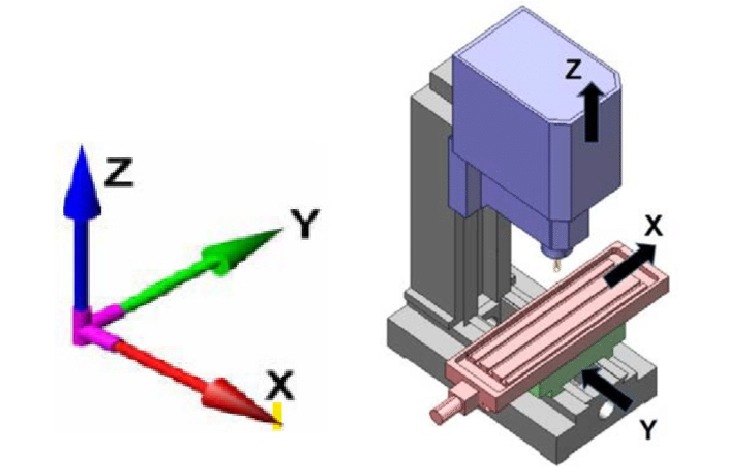
Features
- Enhanced flexibility with additional tool movement.
- Live tooling capabilities (rotating tools for milling).
- Suitable for parts requiring multiple operations.
Advantages
- Greater precision for intricate designs.
- Reduces the need for secondary machining processes.
- Versatile for medium-complexity parts.
Applications
These lathes excel in producing components like valves, fittings, and custom parts for medical devices or machinery.
Multi-Axis CNC Lathes (4-Axis, 5-Axis, and Beyond)
Overview
Multi-axis CNC lathes, such as 4-axis and 5-axis machines, offer advanced capabilities by incorporating additional rotational axes (e.g., A-axis or B-axis). These machines can handle highly complex geometries in a single setup.

Features
- 4-axis lathes: Add a rotational axis for the tool or workpiece.
- 5-axis lathes: Enable simultaneous movement across five axes.
- Often equipped with live tooling and sub-spindles.
Advantages
- Exceptional precision for complex parts.
- Reduced setup time and improved efficiency.
- Capable of producing intricate shapes without repositioning.
Applications
Multi-axis CNC lathes are ideal for aerospace (turbine blades), automotive (engine components), and medical industries (implants). For example, our own CNC 5-axis machining centers, like the DU, DV, and DC series, showcase this technology’s potential for high-end manufacturing.
CNC Swiss Lathes
Overview
Also known as Swiss-type or sliding headstock lathes, these machines are designed for precision machining of small, slender parts. The workpiece is supported by a guide bushing, minimizing deflection during cutting.
Features
- Sliding headstock for feeding bar stock.
- High-speed spindle for rapid production.
- Multiple tools operating simultaneously.
Advantages
- Unmatched accuracy for small-diameter parts.
- Excellent for long, thin components.
- High productivity for mass production.
Applications
Swiss lathes are popular in watchmaking, electronics, and medical fields for creating tiny screws, pins, and connectors.
CNC Turret Lathes
Overview
CNC turret lathes feature a rotating turret that holds multiple tools, allowing quick tool changes without manual intervention. This design enhances efficiency for high-volume production.
Features
- Turret with 8–12 tool stations.
- Automated tool switching.
- Often paired with live tooling.
Advantages
- Faster cycle times due to rapid tool changes.
- Versatile for diverse operations (turning, milling, drilling).
- Durable for continuous use.
Applications
Used in automotive and industrial manufacturing for producing fittings, flanges, and repetitive parts.
CNC Vertical Lathes
Overview
Unlike horizontal lathes, CNC vertical lathes position the workpiece vertically. The spindle is mounted above the workpiece, making them ideal for heavy, large-diameter components.
Features
- Vertical orientation with gravity-assisted chip removal.
- Large workpiece capacity.
- Often equipped with multiple spindles or turrets.
Advantages
- Handles heavy and oversized parts with ease.
- Improved stability during machining.
- Efficient for large-scale production.
Applications
Common in industries like energy (wind turbine hubs) and construction (large gears or rings).
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a CNC Lathe
Selecting the right CNC lathe depends on your specific needs. Here are some factors to keep in mind:
- Complexity of Parts: Simple parts may only require a 2-axis lathe, while intricate designs demand multi-axis machines.
- Production Volume: High-volume runs benefit from turret or Swiss lathes, while low-volume projects suit basic models.
- Material Type: Heavy-duty materials like steel may require vertical or multi-axis lathes for stability and power.
- Budget: 2-axis lathes are more affordable, while advanced 5-axis machines represent a larger investment.
- Space and Setup: Vertical lathes save floor space for large parts, while Swiss lathes are compact for small-scale precision.
Trends in CNC Lathe Technology
The CNC lathe industry is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in automation, software, and materials. Multi-axis machines are becoming more accessible, enabling smaller manufacturers to tackle complex projects. Additionally, integration with Industry 4.0 technologies—like IoT and real-time monitoring—enhances productivity and reduces downtime. As demand for precision and efficiency grows, manufacturers are prioritizing quality components and rigorous testing to meet global standards.
Conclusion
CNC lathes are a vital part of modern manufacturing, offering a range of options to suit diverse needs. From the simplicity of 2-axis lathes to the sophistication of 5-axis and Swiss-type machines, each type brings unique strengths to the table. By understanding their differences, you can make informed decisions to optimize your production process.
At Dongguan HIRUNG Precision Machinery Co., Ltd., we’re proud to contribute to this dynamic industry. Since entering the global market in 2015, we’ve delivered high-quality CNC lathes and machining centers to 33 countries, guided by our motto: “Let the world fall in love with Chinese-made machine tools!” Our EL-series CNC lathes, for instance, reflect our commitment to precision, durability, and customer satisfaction—qualities that help manufacturers worldwide achieve their goals.